CoreJS: Inheritance and Subclassing
19 Aug 2015Review: Constructors and Prototypes
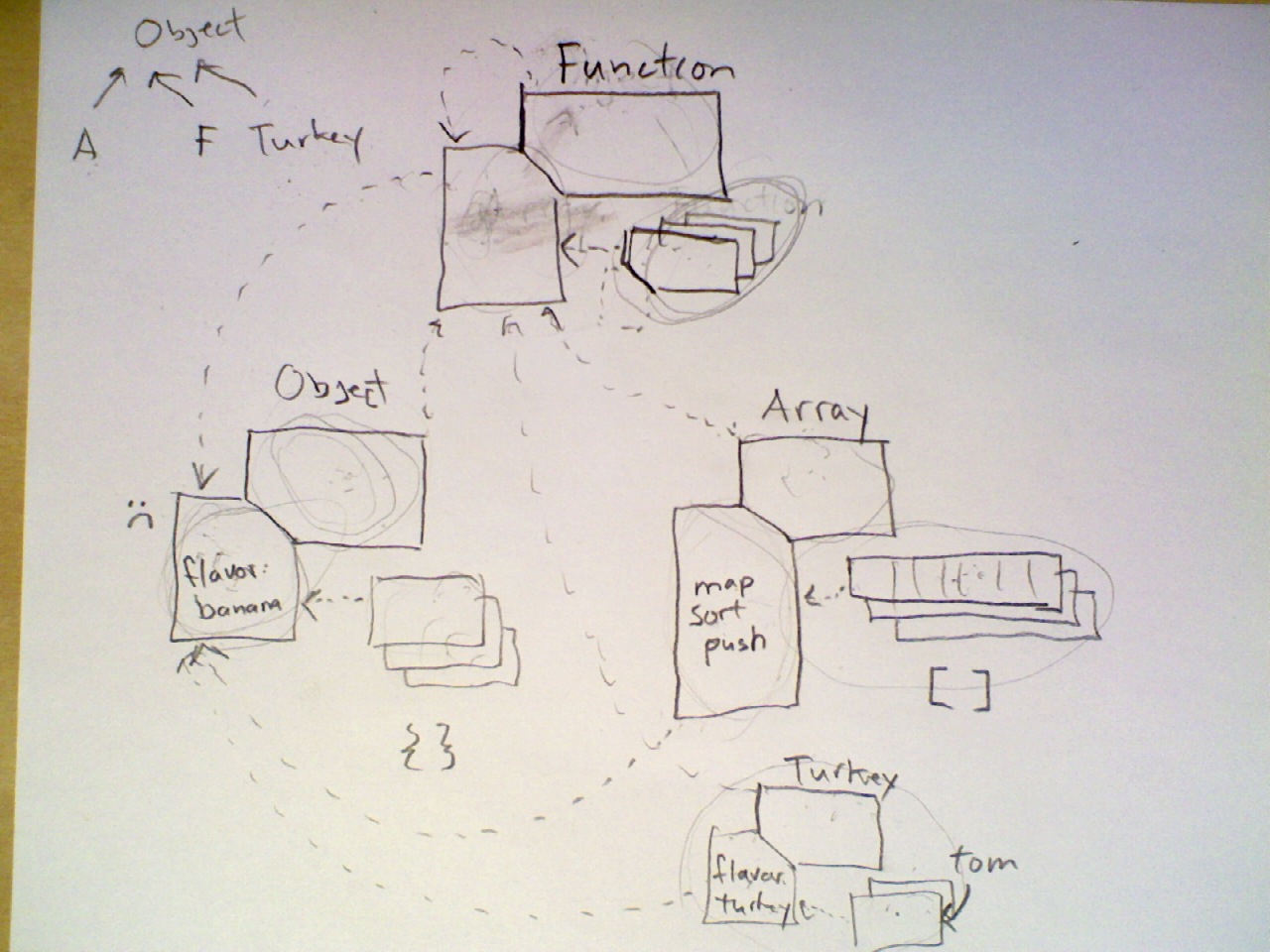
With your team, describe the three roles objects can play in a Javascript "class" and summarize the relationship between each pair:
Constructor vs. Instance
Constructor vs. Prototype
Prototype vs. Instance
Built-in Subclasses
Use the expressions below to infer the inheritance relationships between various Javascript classes:
Object instanceof Object
Object instanceof Function
Array instanceof Array
[] instanceof Array
[] instanceof Object
{} instanceof Object
{} instanceof Function
null instanceof Object
Function instanceof Function
Function instanceof Object
new Number instanceof Object
new String instanceof String
new String instanceof Object
Formulate a hypothesis about how operator instanceof works.
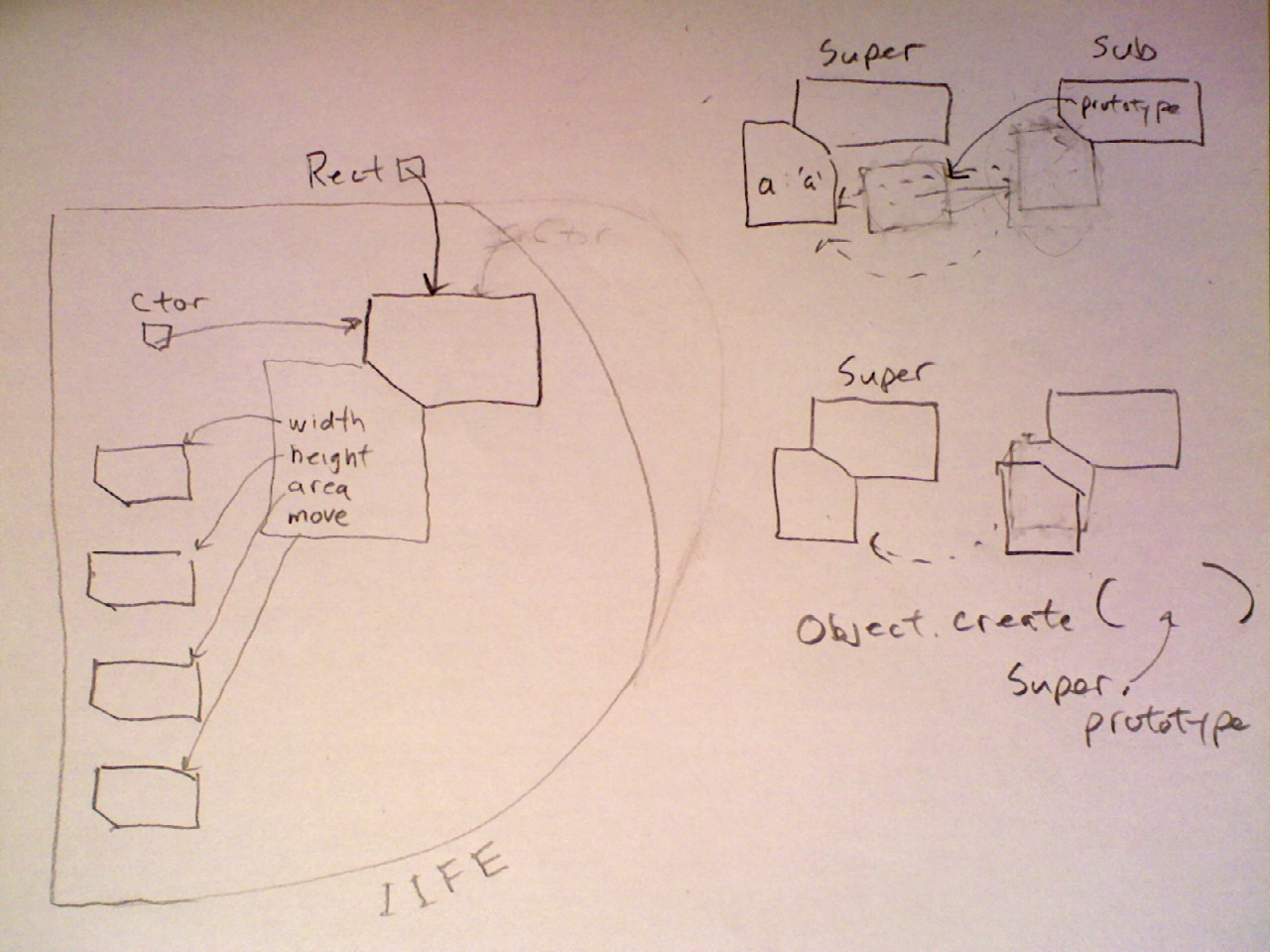
Implementing Inheritance
Here is a module (IIFE) which provides a constructor Rect which builds rectangle instances. The instance methods are shared but linked directly to each instance.
var Rect = (function() {
function Ctor(l,b,r,t) {
this.l = l;
this.b = b;
this.r = r;
this.t = t;
this.width = width;
this.height= height;
this.area = area;
this.move = move;
}
var width = function() {
return this.r - this.l;
}
var height = function() {
return this.t - this.b;
}
var area = function() {
return (this.width() * this.height());
}
var move = function(dx,dy) {
this.l += dx;
this.r += dx;
this.b += dy;
this.t += dy;
}
return Ctor;
})()
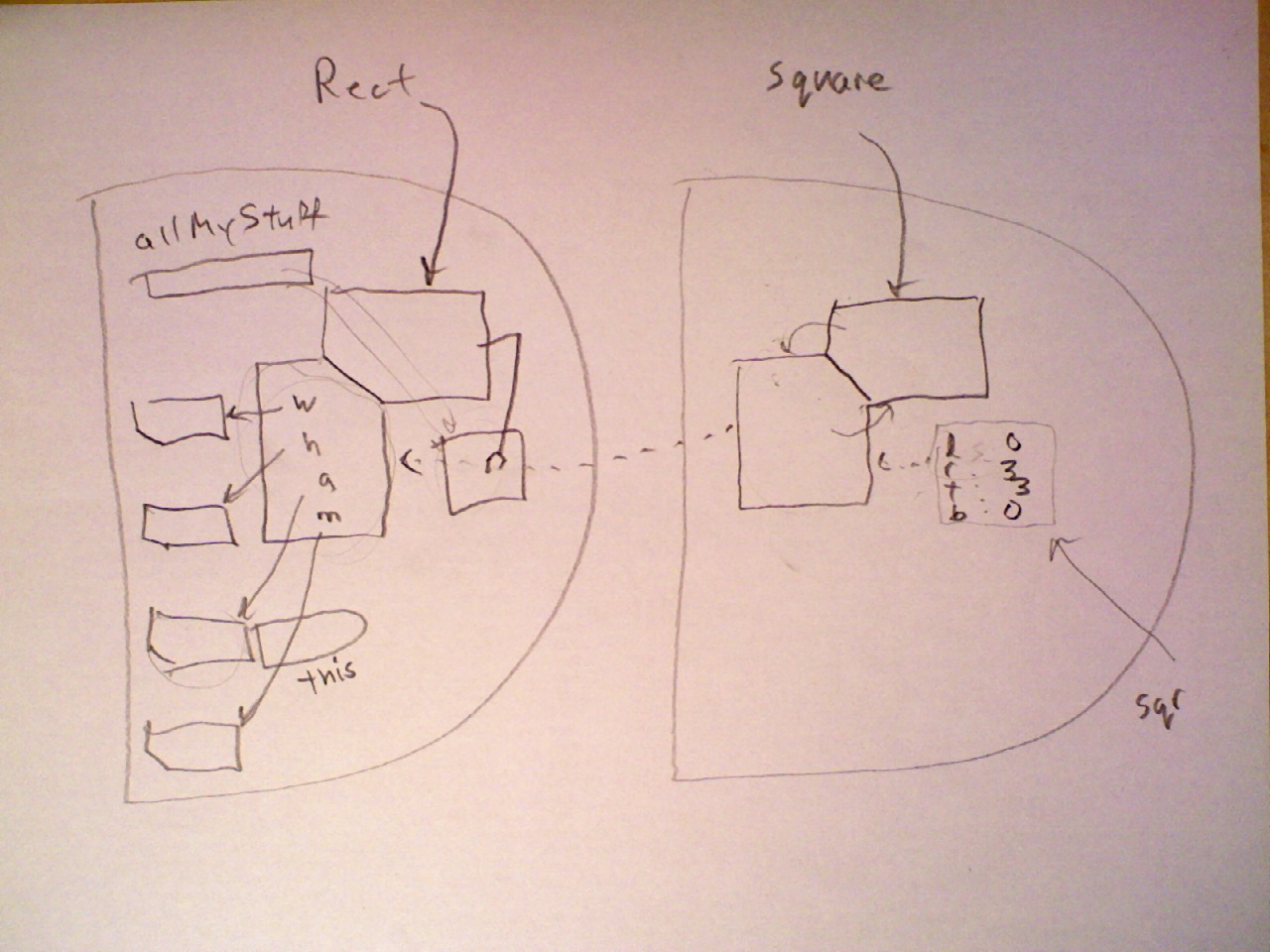
Modify the Rect module so that all instance methods are inherited from a prototype.
In a new IIFE, implement a subclass of
RectcalledSquare. TheSquareconstructor needs only three parameters:Square(left,bottom,size), and it should call the parent class constructor (Rect(left,bottom,right,top)) to set the new instance's properties. A Square instance should inherit thewidth,height,area, andmovemethods of Rectangles without needing any changes.Within the Square module, add an instance method
sizewhich acts as both a getter and setter for a square's size. That is,square.size()should return the current size of square, andsquare.size(num)should set the size to num.For the moment, disable your Square module (by commenting it out or disabling the call operator () which triggers the IIFE). Now Modify the Rect module so that the
Rectconstructor maintains a list of every instance it ever creates. Attach a class methodeveryto constructorRectwhich returns that list.When finished, you should be able run the following sequence:
var r1 = new Rect(0,0,1,1), r2 = new Rect(0,0,2,2), r3 = new Rect(0,0,3,3), all = Rect.every(); //list of r1,r2,r3 all[0] === r1; //trueNow reactivate your Square module and then re-run the sequence above. What is the value of
all[0]===r1? What happened?Notice that constructor
Squaredoes not inherit the class method from its parent classRect! Implement the class methodeveryforSquareas well, so thatSquare.every()will return all squares ever built.
Object.create
Modify constructor
Squareto useObject.createinstead ofnew Rectwhen making Square's prototype. Does that fix the problem in #5 above?Return to your earlier simulation of the new operator, which we approximated like this:
function fakeNew(ctor,arg) { var instance = {}; instance.__proto__ = ctor.prototype; ctor.call(instance,arg); //does initialization return instance; };Simplify
fakeNewby usingObject.create.
Overriding Inheritance
Consider the module below which implements a simplified Deque class:
var Deque = (function () {
function Deque (vals) {
// unprotected version
this.array = vals.slice();
}
Deque.prototype.top = function () {
if (this.array.length)
return this.array[this.array.length-1];
}
Deque.prototype.bottom = function () {
if (this.array.length)
return this.array[0];
}
Deque.prototype.push = function(val) {
return this.array.push(val);
}
Deque.prototype.pop = function() {
return this.array.pop();
}
Deque.prototype.unshift = function(val) {
return this.array.unshift(val);
}
Deque.prototype.shift = function() {
return this.array.shift();
}
return Deque;
})();
In a new IIFE, implement a subclass of
DequecalledStack. A Stack is a kind of Deque which is top-access only, affording Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) storage. A Stack instance will inherit all the method of Deque, but you'll need to disable the three methods which allow access to the bottom of the Stack.In a similar way, implement another subclass of
DequecalledQueue. A Queue is a kind of Deque which affords First-In-First-Out storage, where items are pushed onto the top and shifted from the bottom. Only the bottom of a queue is visible.
Automated Inheritance through extend
The process of generating a subclass can be automated by giving every function a method to extend it with a subclass. We'll use a variant of that pattern later with Backbone, but here is a rough approximation of how it works:
Function.prototype.extend = function(protoProps) { // method of any function...
var Super = this; //the function to be subclassed
function Ctor() { // the subclass ctor
Super.call(this);
}
// Make Ctor a subclass of Super:
var proto = Object.create(Super.prototype); //the subclass prototype
Ctor.prototype = proto;
proto.constructor = Ctor;
// Copy protoProps into subclass prototype:
//_.extend(proto,protoProps);
// OR
for (var prop in protoProps) {
proto[prop] = protoProps[prop];
}
return Ctor;
}
Here is an example of it in use:
function Duck() {}
Duck.prototype.feet = 2;
Duck.prototype.noise = 'quack';
var MutantDuck = Duck.extend({feet:3});
var duck = new MutantDuck();
duck instanceof MutantDuck; //true
duck instanceof Duck; //true
// Inherited from MutantDuck:
duck.feet; // 3
duck.hasOwnProperty('feet'); //false
// Inherited from Duck:
duck.noise; // 'quack'
duck.hasOwnProperty('noise'); //false
Samples
Diagrams